
An accounting journal entry is the written record of a business transaction in a double entry accounting system. Every entry contains an equal debit and credit along with the names of the accounts, description of the transaction, and date of the business event. Recording transactions begins with source documents like purchase and sales orders, bills, invoices, and recording in accounting cash register tapes. Once you gather these documents, you can record the transactions using journals, ledgers, and the trial balance. If you are a very small company, you may only need a cash register. The information can then be consolidated and turned into financial statements.
What Is Double-Entry Bookkeeping?
You can even link online accounting software to your bank account so the data flows Bookstime through automatically. You make an adjusting journal entry to update account balances before preparing financial statements at the end of an accounting period, so the statements will include the correct information. This step is significant because it involves preparing financial statements. Through the recording phase, businesses can document their financial transactions in a systematic manner.
General Ledgers
The total of all credits and debits during the course of the business cycle makes up the trial balance. Accounting is the process of keeping track of your business’s financial transactions. It helps you to understand how money comes in and how it goes out. Accounting is popularly regarded as “the language of business” because it doesn’t just help you keep track of your money, but also helps you make informed decisions about your business. To speed up action, you may hire accounting professionals or purchase accounting software to ensure accurate financial audits and reporting. You can choose to manage your business accounting by hiring an in-house accountant or CPA.
Experience seamless accounting with Zoho Books

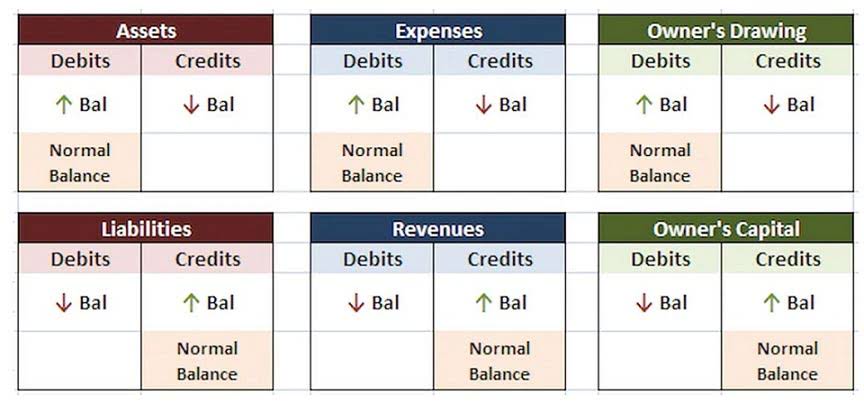
The key is practice—think of debits as “increases” in what you own or spend and credits as “increases” in what you owe or earn. Using visual aids like T-accounts can also help clarify these concepts. By adopting double-entry accounting, businesses gain not just a bookkeeping tool but a strategic advantage that supports growth, accuracy, and accountability. Double-entry systems create detailed, organized records for every transaction, making it easier to trace the flow of funds.

It’s important to keep accurate and detailed records of all your business transactions. Doing so will help you know whether you’re conducting business properly. This focuses on the use and interpretation of financial information to make sound business decisions. It’s similar to financial accounting, but this time, it’s reserved for internal use, and financial statements are made more frequently to evaluate and interpret financial performance. Accounting is the process of recording, classifying and summarizing financial transactions. It provides a clear picture Certified Public Accountant of the financial health of your organization and its performance, which can serve as a catalyst for resource management and strategic growth.
- It specifies the date of each transaction, the accounts credited or debited, and the amount involved.
- Income and expenses that flow in and out of your bank account are generally straightforward.
- This is the act of tracking and reporting income and expenses related to your company’s taxes.
- Whether your accounting period is monthly, quarterly, or annually, timing is crucial to implementing the accounting cycle properly.
Bank Reconciliation
Accounting records include records of assets and liabilities, monetary transactions, ledgers, journals, and any supporting documents such as checks and invoices. If you use accrual accounting, you’ll want to record purchase invoices as soon as they come in and sales invoices as soon as they go out. That way amounts, dates, taxes, and customer and vendor information are automatically recorded in the software at time of issue. If your business is ever audited, or if you need to prepare financial statements like the balance sheet and income statement, double-entry makes it a breeze. It ensures that all the data you need is already categorized and balanced, saving time and headaches.

Recording transactions is not the aspect most think about as the hardest of accounting. Despite that, numerous parts of the process serve as potential traps and errors, so paying careful attention to a few basic rules is essential. Whether your accounting period is monthly, quarterly, or annually, timing is crucial to implementing the accounting cycle properly. Mapping out plans and dates that coincide with your accounting deadlines will increase productivity and results.
Preparing the Trial Balance
- An accounting ledger, on the other hand, is a listing of all accounts in the accounting system along with their balances.
- Before you begin bookkeeping, your business must decide what method you are going to follow.
- Accounting information exposes your company’s financial performance; it tells whether you’re making a profit or just running into losses at the end of the day.
- These assets are depreciated each year to reflect that they’re losing value, and the depreciation can be claimed off taxes.
- It’s how you track the money flowing in and out of your business, usually in the form of sales and expenses but also from loans and investments.
- Bookkeepers or accountants are often responsible for recording these transactions during the accounting cycle.
This can be a great option if you want to ensure your books are in order, and that your company’s financial information is accurate, but it does come with some drawbacks. For one thing, the cost of hiring someone like this can be a substantial burden on your business’s finances. To complete the process, you’ll want to record the business transaction as a journal entry in the correct journal. Don’t forget to include the date of the transaction and a brief description of the financial event you’re recording. The income statement, also known as the statement of operations or profit and loss statement, shows the company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period of time. The purpose of the income statement is to measure the profitability of the company.



Kommentare von reda