
Book value is an accounting term, a metric investors use in fundamental analysis. The term can be confusing, though, because it has one meaning when referring to an entire company and a slightly different meaning when referring to an asset. On the other hand, if a company with outdated equipment has consistently put off repairs, those repairs will eat into profits at some future date. This tells you something about book value as well as the character of the company and its management.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
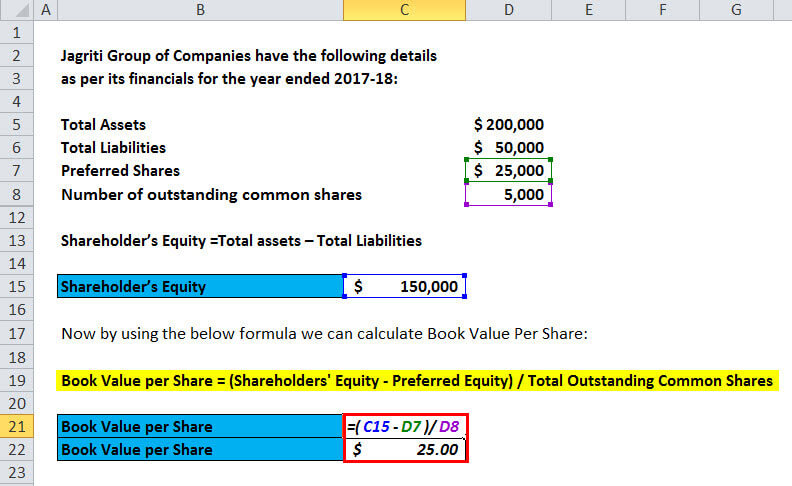
Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities. The 1st part will be to find the equity available to its common shareholders.
Formula to Calculate Carrying or Book Value
Market values for many companies actually fell below their book valuations following the stock market crash of 1929 and during the inflation of the 1970s. Relying solely on market value may not be the best method to assess a stock’s potential. Suppose that XYZ Company has total assets of $100 million and total liabilities of $80 million. If the company sold its assets and paid its liabilities, the net worth of the business would be $20 million. The book value literally means the value of a business according to its books or accounts, as reflected on its financial statements. Theoretically, it is what investors would get if they sold all the company’s assets and paid all its debts and obligations.
- When the market value is near or less than the book value, the P/B ratio will be 1 or less, signaling that the stock may be undervalued.
- Investors who rely heavily on book value analysis are typically looking for good stocks that are temporarily underpriced by the investment community.
- Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
In this scenario, the market is giving investors an opportunity to buy a company for less than its stated net worth. Book value represents the value of assets and liabilities at the date they are reported in a company’s documents. Book values are important for valuation purposes because they are based on accounting principles that are calculated consistently for all companies. For most assets and liabilities, book values are based on the historic cost of items.
The Book Value formula calculates the company’s net asset derived by the total assets minus the total liabilities. Alternatively, Book Value can be calculated as the users of accounting information internal external examples total of the overall Shareholder Equity of the company. A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value.
With increases in a company’s estimated profitability, expected growth, and safety of its business, the market value per share grows higher. Significant differences between the book value per share and the market value per share arise due to the ways in which accounting principles classify certain transactions. While corporate debt holders and preferred shareholders are entitled to a fixed series of cash payments, the cash flow in excess of those amounts is essentially the property of the common shareholders. The value of a common stock, therefore, is related to the monetary value of the common shareholders‘ residual claim on the corporation – the net asset value or common equity of the corporation.
The two numbers can be different, usually because the issuer has been buying back its own stock. In this case, the shares outstanding number is stated at 3.36 billion, so our BVPS number is $71.3 billion divided by 3.36 billion, which equals $21.22. Each share of common stock has a book value—or residual claim value—of $21.22. At the time Walmart’s 10-K for 2012 came out, the stock was trading in the $61 range, so the P/BVPS multiple at that time was around 2.9 times. Equity investors often compare BVPS to the market price of the stock in the form of the market price/BVPS ratio to attribute a measure of relative value to the shares. Keep in mind that book value and BVPS do not consider the future prospects of the firm – they are only snapshots of the common equity claim at any given point in time.
Spreading your money across industries and companies is a smart way to ensure returns. Book value shopping is no easier than other types of investing; it just involves a different type of research. The best strategy is to make book value one part of what you are looking for as you research each company.
It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers‘ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth. Therefore, the market value, which is determined by the market (sellers and buyers) and represents how much investors are willing to pay after accounting for all of these factors, will generally be higher. Book value per common share (or, simply book value per share – BVPS) is a method to calculate the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders‘ equity in the company. The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and total liabilities, and not its share price in the market.



Kommentare von reda